All analogies sacrifice accuracy in order to convey some aspect that is considered significant in this case the notion that gravity is caused by curvature of space time.
General relativity rubber sheet.
It seems topology was established before special or general relativity was formulated.
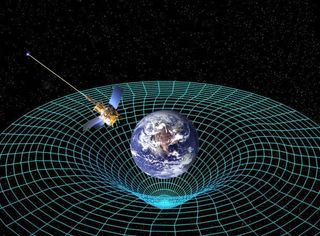
Imagine a large rubber mat with a bowling ball sitting on it.
In 1919 british expeditions to africa and south america observed a total solar eclipse to see if the position of stars near the sun had changed.
The rubber is a two dimensional representation of the fabric of spacetime.
But on a rubber sheet that is deformed by a.
General relativity is one of the more challenging ideas in science.
A common analogy is placing a heavy object on a stretched out rubber sheet causing the sheet to bend downward.
The most common method of describing his theory is called the rubber sheet model.
Einstein instantly became world famous.
Who came up with the idea of the rubber sheet analogy in relativity.
In general relativity energy and mass have curvature effects on the four dimensions of the universe spacetime.
General relativity predicted that light would bend in a gravitational field.
The ball stretches the rubber to form a nice curved bowl shape.
The observed effect was exactly what einstein had predicted.
Some there have wondered if it was the rubber sheet geometry as topology was described as apparently that may have perhaps unconsciously given birth to the idea as an analogy.
This curvature gives rise to the gravitational force.
Imagine the old bowling ball analogy for general relativity and spacetime.
The bowling ball represents a large mass like a planet or our sun.
Rubber sheet with a bowling.
That s hardly surprising given the complexity of the mathematics involved.
Kentuckyfc writes general relativity is mathematically challenging and yet widely appreciated by the public.
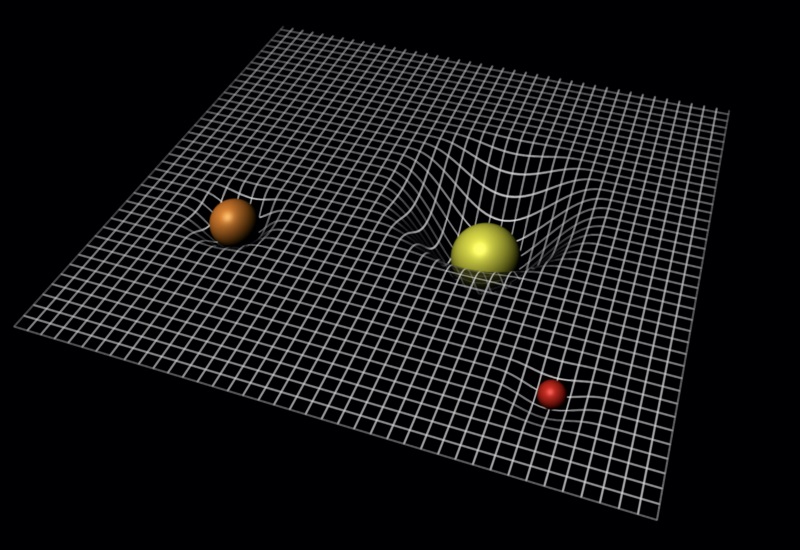
That the warping of spacetime to produce gravity is like the deformation of a rubber sheet by a central mass.
This state of affairs is almost entirely the result of one the most famous analogies in science.